
The working acceptance limits for acceptance values (AV) are determined using the critical values at, for example, 95% coverage over the corresponding AV distributions. However, validity of such limits needs to be elaborated.

The working acceptance limits for acceptance values (AV) are determined using the critical values at, for example, 95% coverage over the corresponding AV distributions. However, validity of such limits needs to be elaborated.

Research suggests that radiation can have a significant impact on the composition and rheology of hydroxyethyl cellulose-based medicinal gels.

This article describes a new, combined, quantitative method for assessing excipient risks that has been developed by the authors as one possible risk evaluation method.

The following study describes a methodology to establish, control, and characterize an aerosolized bioburden within a test chamber and determine the settling rate of the bioburden.

A new algorithm uses a statistical approach to critical process parameter assessment, allowing for faster, more consistent, and less subjective critical process parameter quantification, visualization, and documentation.
In Part I of this article series, the authors discussed the regression control chart method for identifying out-of-trend data in pharmaceutical stability studies. In Part II, the by-time-point method and the multivariate control chart method are investigated, and improved approaches are suggested. The method is illustrated using real data sets.

In Part I of this article series, the regression control chart method for identifying out-of-trend data in pharmaceutical stability studies is investigated, and an improved approach is suggested.

The authors demonstrate that a proper measure of HPMC solution concentration is its electrical conductivity rather than its viscosity.

This study shows that the presence of API lumps can be detected by inline NIR, and elaborates on why NIR sensor dimensions and actual measured sample volume by the NIR sensor are important variables for adequate interpretation of obtained results.

Amid contentious debate about “fake news,” peer-review papers offer vital, objective insight.

The author describes how to establish acceptance limits for acceptance value (AV) data for process validation batches, typical characteristics of AV distributions, and how to derive relevant constants for AV control charts in annual product review and continued process verification reports.

Incorporating structural constraints into pharmacokinetic studies of iron sucrose formulations.
In this study, the authors describe a forensic microscopy approach to characterize particles that were visually observed during stressed stability testing of an ophthalmic solution formulation.
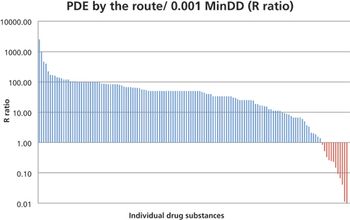
In this study, the authors investigated the relationship between the 0.001 MinDD and the PDE values for 140 drug substances as an attempt to identify high-risk groups of products for patient safety. This comparison can serve as a method for prioritization of APIs for development of PDEs.

The primary impact of using the covalidation model is the expedited analytical method qualification of both the transferring and receiving laboratories.

This study investigated the stability of solid lactose stored under high temperature and humidity conditions.
This article introduces the concepts of pooled variance and the central limit theorem, which are intended for establishing acceptance criteria for blend uniformity data of granular powder blends when a significant degree of sampling bias is involved.

The authors present a set of statistical decision rules based on linear regression models that can be implemented in an automated trend system to assist stability studies.





The Uniformity of Dosage Units test is used to evaluate content uniformity or weight variation or dosage forms such as tablets and capsules. The author introduces two different acceptance value limits (n = 10 and 30) in this article.

This article will clarify reasonable expectations for the responsibilities of topical product formulation developers and for excipient suppliers regarding the information and samples for experiments needed for QbD.

This article will equip the excipient vendor with an understanding of QbD from the perspective of the topical pharmaceutical product manufacturer.

Swab recovery parameters are reviewed in detail to define best practices and highlight common mistakes to assure successful recovery studies using a risk-based approach.
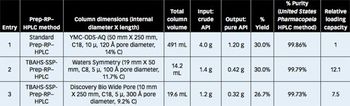
This paper describes a unique Prep-rP-HPLC technique that uses a C-18/C-8 derivatized silica coated with a hydrophobic quaternary ammonium salt or quaternary phosphonium salt that acts as an additional/surrogate stationary phase (AsP/ssP).

The authors' directed isotopic synthesis is one example of how molecular isotopic engineering can be used to predetermine the discrete isotopic ranges of biopharmaceutical products.

This article presents recommendations based on a program that was set up to qualify members of a large, diverse team at one oral solid-dosage-form manufacturing facility.

The authors discuss the concept design of a versatile, sustainable, small-scale facility in Malta that conforms to the European Union’s current good manufacturing practices.