
This paper provides an in-depth overview of the anatomical structure and functional dynamics of renal filtration, secretion, and reabsorption processes that govern drug clearance.

This paper provides an in-depth overview of the anatomical structure and functional dynamics of renal filtration, secretion, and reabsorption processes that govern drug clearance.

The authors performed interference and enhancement testing using a formulated alkaline and acid cleaner, as well as common biopharmaceutical process residues.
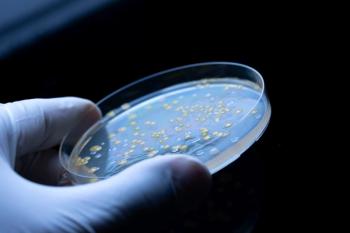
This article explores the impact of test volume, microbial distribution, and dilution errors on bioburden testing variability. It presents statistical approaches to estimate percentage error and discusses strategies to optimize microbial enumeration techniques in biopharmaceutical quality control.

The ‘full tolerance coverage method’ is introduced as a coverage estimation approach for assessing the uniformity of dosage units from large sample sizes, ensuring that no dosage unit exceeds the specification range.

This paper explores the legal and regulatory framework around 3D drug printing, particularly for personalized medicine, considering regulatory compliance, business concerns, and intellectual property rights.

Various microorganisms, including molds and bacterial spores, were tested on stainless-steel coupons and demonstrated 2–6 log reductions with one-minute wet-contact times.

In this paper, the authors introduce a method that combines ion exchange chromatography with an easier-to-perform, simpler one-step post-column derivatization that is selective to nitrite and visible spectrophotometric detection to allow high sample loading volumes without affecting resolution.

The growing use of continuous manufacturing in the pharmaceutical industry merits a review of the application of dry cleaning and sanitization methods, especially for non-sterile oral solid drug product manufacturing of dry powders.
A statistical analysis for determining an expiration date can be applied to replicates or their corresponding averages as suggested in industry guidelines.

This study reviews changes in in-country testing (registration testing, import testing) requirements and analyzes current trends. In the context of international harmonization of good practices and standards as well as the improved information exchange between national regulatory authorities, in-country testing is considered outdated and redundant in many cases.

This study aimed to develop a taste-masked drug resin complex using the ion exchange resin Kyron T-114.

This article introduces that the basic technique for tolerance interval is implemented using the conventional range 85–115% LC where the proposed range in the PF is not taken into account.
One of the main purposes of stability testing is to establish shelf life for these drug products. The goal of this paper is to create an Excel spreadsheet, which can be used for statistical testing of more than three stability batches for poolability.
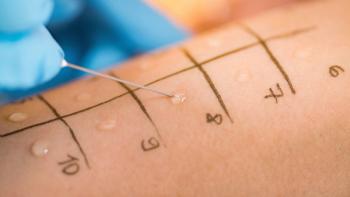
FDA’s new guidance on in-vitro permeation test studies published in October 2022 gives technical and statistical requirements for conducting these tests to compare topical generic drugs with their reference products.
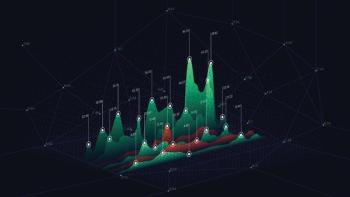
This paper demonstrates how assay data sets of a formulated liquid product, drug substance, and an impurity, obtained from combined accuracy-precision studies, are evaluated to calculate statistical intervals (prediction and tolerance intervals) and to graphically display the total analytical error (TAE) to account for the systematic and random errors.

This article discusses the evaluation of paired content uniformity and weight variation data sets using F and T tests to ensure that batches meet compendial requirements.

A fluorescence test method was used to visually evaluate handwashing efficacy. Difficult-to-clean areas on skin such as skin folds and webbing between fingers were identified; specific washing techniques to address problem areas are proposed.

Advancements in soft capsule technology can enable the development of soft capsule formulations, which are becoming the preferred method of oral administration.
It is argued that orthogonal quantitative methods can be used to establish primary working standards. An example details how to calculate the expanded measurement uncertainty (U) for the certified assay value by considering two orthogonal assay methods.
The purpose of this article was to demonstrate the application of a new thermogelling matrix in the healing of wounds.
Researchers demonstrated a new cell lysis method using a novel solution to improve viral vector production.
The author introduces a practical approach to determining the best estimate of probability for passing multiple stage dissolution tests.

Process performance metrics of eight different mechanical devices were assessed to evaluate compliance with regulatory and compendial criteria.
In this study, researchers evaluated the colloidal microcrystalline cellulose (cMCC) suspending agent—a co-processed material of microcrystalline cellulose and sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (NaCMC)—by using a representative pharmaceutical-grade commercial version of cMCC.

The authors introduce the idea of asymmetrical tolerance intervals as an aid in fully assessing product performance relative to product or process requirements.

Part two of this article series shows how traditional statistical process control rules can be relaxed or adjusted to allow charting and evaluation of real-life data of pharmaceutical processes with a reduced number of false alarms.

Part 1 of this article series demonstrates, using real-world process data, that the four fundamental assumptions underlying the classical Shewhart control charts—randomness, independence, constant average, and constant variation—are often not met.

The potential for okra gum as a polymer candidate for new oral drug formulations was evaluated.

A robust selection of which product(s) and equipment to validate for cleaning is the cornerstone of a successful cleaning validation program. A strategy for selection of products and equipment for cleaning validation is presented.

The purpose of this research was to formulate modified liquisolid compacts (MLSC) of RLX for improved dissolution in immediate-release tablet formulations.