
Following its $68-billion acquisition of Wyeth, Pfizer has unveiled detailed plans for its global R&D network, which includes consolidation of its R&D facilities.

Following its $68-billion acquisition of Wyeth, Pfizer has unveiled detailed plans for its global R&D network, which includes consolidation of its R&D facilities.

A smart nanocage that can be filled with a medicinal substance and then activated using light has been developed by US researchers.

A new drug delivery method developed by scientists could enable prescription drugs to be buried inside the body where drug release could be prompted by a biological trigger, such as a drop in blood sugar levels, or activated manually with a pulse of light.

The author discusses control strategies via near infrared instrumentation for continuous mixing, granulation, drying, and extrusion with a more focused detail on mixing.

Semisolid Formulation Development: The CRO Approach - SP Formulations Whitepaper

NIR Prediction of Solid Dosage Form Dissolution Profiles - Foss Whitepaper

Bulk Inspection of Tablets-Symetix Application Note

A US Food and Drug Administration guidance issued Tuesday provides new recommendations to applicants who wish to designate proposed products as orally disintegrating tablets (ODTs).

Recent advances in SEM, particularly the incorporation of automation and software, have made simpler, lower-end SEM instruments easy to operate and have improved the capabilities of larger, sophisticated instruments.

Traditional tablet presses do not measure tablets' tensile strength, yet this characteristic strongly influences tablet quality. The author describes a compression technique that accounts for tensile strength and produces tablets with consistent weight and disintegration time.

Chemical imaging of solid dosage forms has become a powerful analytical tool for the development of solid dosage forms.

To ensure an effective treatment, a patient often must take equal doses of an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) at regular intervals.
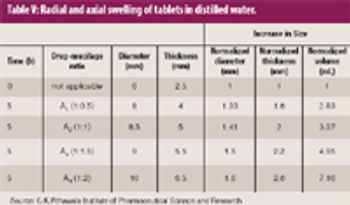
Natural gums and mucilage have been widely explored as pharmaceutical excipients. The goal of this study was to extract mucilage from the leaves of Aloe barbadensis Miller and to study its functionality as an excipient in pharmaceutical sustained-release tablet formulations.

Ranbaxy received full market approval from the US Food and Drug Admnistration for its anti-infective agent ?Clarithromycin? oral suspension.
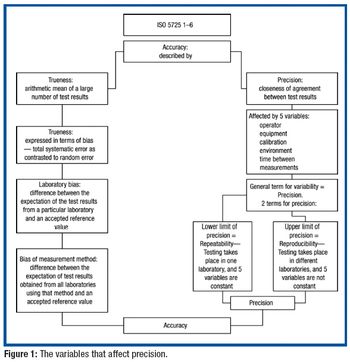
USP applies metrological principles to the dissolution procedure alone and in collaborative studies to understand and minimize potential sources of variability.
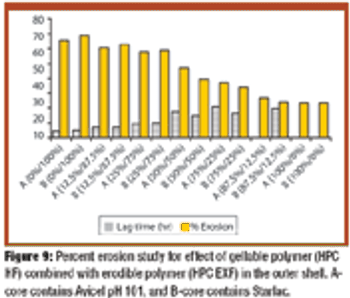
The authors prepared and tested press-coated tablets with various weight ratios of ethylcellulose to hydroxypropylcellulose (HPC) and various ratios of two different batches of HPC as an outer coating shell and fillers in core tablets. The tablets were examined for changes in time lag and release patterns of salbutamol sulfate.

A wealth of citations helps illustrate the applicability of the analytical methods and also highlights their pitfalls.

Just because the wheels are turning doesn't mean they're going forward.
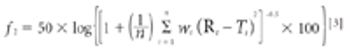
The objectives of this study were to prepare and characterize inclusion complexes of lovastatin with hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HPβ-CD) and to study the effect of the complexes on the dissolution rate of lovastatin (LVS). The findings suggest that LVS's poor dissolution profile can be overcome by preparing its inclusion complex with HPβ-CD.
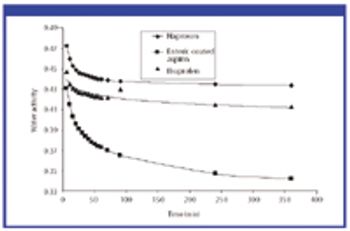
For solid oral-dosage forms, water testing usually is performed to control the chemical, physical, or microbiological properties of the drug product. Measurements of total water as made with Karl Fischer (KF) techniques is not needed and water-activity often will provide a better correlation with changes in chemical, physical, or microbiological properties than KF techniques. In these cases, water activity testing can easily replace KF testing. Water-activity measurements are nondestructive, require little labor, and the equipment required is generally inexpensive. Only a few simple checks are needed to ensure the validity of measurements. Strategies for implementing water activity testing are described.

Pfizer's restructuring plan provides yet another example of new supply-chain strategies by the pharmaceutical majors, which involve rationalization of manufacturing facilities and cost improvement. A review of these moves, an outlook for the pharmaceutical market in 2007, and analysis of US pharmaceutical production and trade.
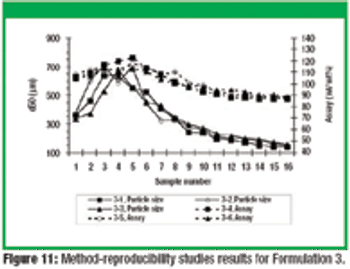
This article describes the design and development of a material-sparing fluidization segregation tester for use with pharmaceutical powders. This tester offers several improvements over the current ASTM standardized test practice. Less than 20 mL of material is required to characterize the fluidization segregation potential of a sample. Features of the tester include powder containment for potent compounds, in-process monitoring of the fluidization conditions, and sample retrieval without the need for subsampling or riffling for typical analyses.

AAPS, San Antonio (Oct. 30)-Aiming to provide a greater understanding of coating processes, speakers at the 20th Annual Meeting of the American Association of Pharmaceutical Scientists presented some of the difficulties, tools, and strategies for obtaining adequately uniform films in pan and fluid-bed coating processes.

San Antonio, TX (Nov. 1)-Though the US Food and Drug Administration's final guidance on process analytical technology (PAT) was published in Sept. 2004, companies are still unsure about how exactly to implement PAT in their processes.
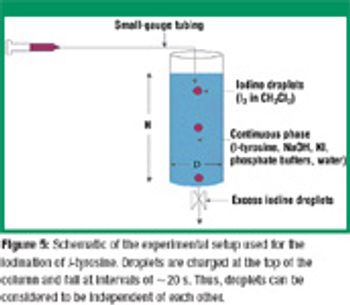
Understanding the impact of reactive mass transfer and local flow in multiphase systems is crucial for maximizing reaction selectivity and minimizing the formation of byproducts. The authors study the influence of mixing on fast liquid–liquid reactions. The iodination of L-tyrosine was used to demonstrate the relationship of droplet size and shape on reaction selectivity and to verify computational predictions. By understanding that droplet dynamics affect the yield and selectivity of fast reactions, the formation of byproducts can be minimized by optimizing operating parameters.