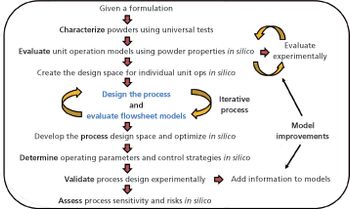
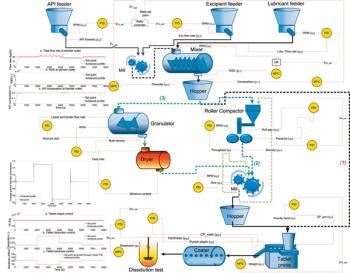
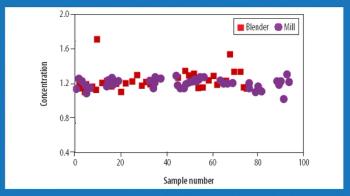
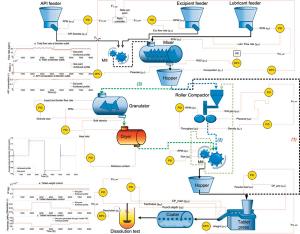
Prior to use in a continuous manufacturing system for oral solid dosage forms, loss-in-weight feeders need to be tested and validated to understand the performance capabilities of a given material–feeder combination. In this article, the proper strategy for set-up and optimization of a loss-in-weight feeder is demonstrated for a range of materials. The optimized set-up of the feeders was demonstrated to provide suitable performance for even the most challenging, poorly flowing materials.