The sixth in a series of eight case studies from the Product Quality Research Institute focuses on packaging line GMP optimization.

The sixth in a series of eight case studies from the Product Quality Research Institute focuses on packaging line GMP optimization.

Training cleanroom operators can be one of the most challenging aspects to maintaining cleanroom conditions. PTE speaks to Neal Wesley, technical director at SCM Pharma, to find out the best practices for training and ensuring continued compliance.

Jerold Martin, senior vice president global technical affairs, at Pall Life Sciences, explains the importance and impact of single-use systems in sterile environments.

Millions of pounds worth of products are at risk if contamination occurs in a cleanroom environment. According to an independent consultant (Cleanroom Management Associates Inc) for our company, contamination from personnel and equipment, such as wheeled carts and tanks, is a major concern in cleanrooms and controlled environments.

Contamination is almost always related to human error and there is a clear drive to reduce human implications in aseptic operations. This can be achieved in multiple ways.

PTE quizzes Jaime Cassar, cleanroom category manager at Kimberly-Clark Professional Europe, about the importance of sterile garments for cleanroom environments.

When a pharmaceutical supply chain is compromised, there can be disastrous consequences, not only for consumers, but also for manufacturers. Without comprehensive security measures, pharmaceuticals are susceptible to counterfeit, diversion, dilution, tampering and deliberate contamination—ultimately compromising patient safety.

A modular cleanroom construction is typically a freestanding, solid and robust structure that is suitable for use within an existing cleanroom, laboratory, manufacturing area or warehouse.

On Nov. 17, 2011, a bill that would increase penalties for those convicted of trafficking in counterfeit drugs was introduced in the House of Representatives. The Counterfeit Drug Penalty Enhancement Act of 2011, cosponsored by four US Senators and two US Representatives.

The EMA released a concept paper for consultation on Nov. 8, 2011, that recommends a revision to Annex 16 of the Guide to Good Manufacturing of Medicinal Products to address more complicated global supply chains and new falsified medicines legislation.

We have changed the brand of our stoppers for a product that we freeze-dry in vials. Since the change, we have observed a significant increase in rejects for collapsed cakes. Why are the cakes collapsing? What can we do to prevent this problem?

PharmTech's monthly newsletter, Equipment and Processing Report, reviews the Editor's Picks for the November 2011 edition from Sartorius Stedim Biotech and Thermo Fisher Scientific.

Implementing a zero-waste strategy is not merely an option, it can be seen as a crucial business imperative.

Until now, the industry has adhered to the tradition of producing three batches of product to validate its manufacturing processes. But FDA?s new process-validation guidance does not prescribe any number of batches that is necessary for compliance.

On Sept. 27, 2011, FDA sent Genentech a Form 483 listing several violations at the company's South San Francisco, California, plant. The violations included problems with investigations into batch failures, inappropriate equipment design, and insufficient protection against contamination. FDA visited the plant, which produces the cancer drug Avastin, 13 times in September 2011 and made four observations.

Clamor mounts over compromised care and rising costs due to lack of crucial therapies.
Pharmaceutical companies are responding to the high cost of introducing new drugs to market in different ways.

Careful mixing during a product's distillation can help avert trouble from a strong concoction.

Researchers develop various catalytic approaches for improving yield, purity, stereoselectivity, and process conditions.

Novartis AG and Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation have been focusing research efforts on rare diseases since the company was established in 1996.

Pharma companies and their suppliers are tasked with managing an evermore complex clinical-trial material supply chain.
New product reviews for November 2011.
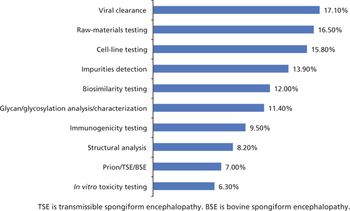
Biosimilar manufacturers need better expression systems and analytical tools to compete.
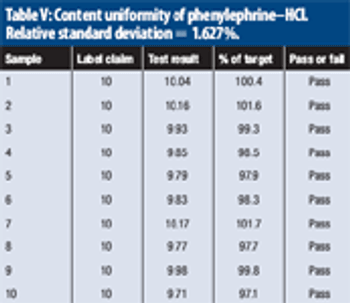
The study evaluates near-infrared analysis of tablets nominally containing 4 mg of chlorpheniramine maleate and 10 mg of phenylephrine hydrochloride per dose.
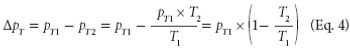
The authors describe the operational qualification of test accuracy with regard to temperature drift using a thermal-compensation algorithm on several freeze dryers.