
References for the article published in the February issue of Pharmaceutical Technology Europe.

References for the article published in the February issue of Pharmaceutical Technology Europe.

Eran Gabbai, CEO and President of Do-Coop Technologies, explains the benefits of a new water-based nanotechnology.

Novartis CEO To Step Down; DSM To Close Netherlands Facility; And More.

FDA Issues Warning Letter To McNeil Healthcare; Charles River Laboratories Will Suspend Operations At Massachusetts Facility.

Could flexible manufacturing change the standards for biopharmaceutical production? To find out, Equipment and Processing Report talked to James Robinson, vice-president of technical and quality operations at biotechnology company Novavax (Rockville, MD).
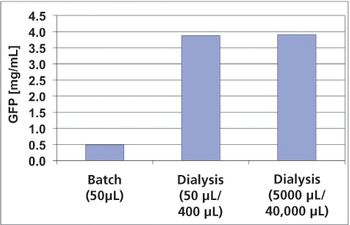
The authors sought to improve the productivity of protein synthesis by using a highly active cell-free extract from Escherichia coli and by optimizing buffer conditions and shaking conditions.

The United States Pharmacopeial Convention is recalling USP 33?NF 28.

Bioject Medical Technologies establishes alliance with MPI Research; Biogen Idec CEO to retire; And More.
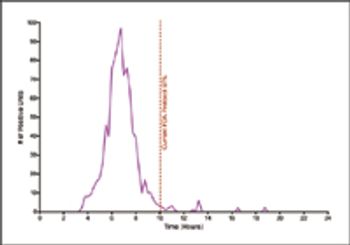
This study used biological indicators containing Geobacillus stearothermophilus spores and a new technology to continuously monitor incubated BIs and record nonsterile results.

Team leaders in FDA's Office of Generic Drugs provide an overview.

Plus, novel dosage forms and emerging trends.
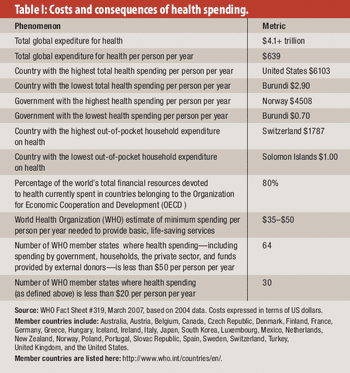
From healthcare to corruption to life expectancy, here's what we can learn from the past decade.

Directors and staff miss the mark when it comes to following procedures.

Tumour-penetrating microparticles (TPM), drug delivery vehicles that have been designed to specifically target and infiltrate peritoneal tumours, are more efficacious than standard chemotherapy, according to our preliminary research data.

BioNanomatrix (Philadelphia) names Edward Erickson president and CEO; and More.

Merck & Co. Acquires Avecia Biologics; Ambrilia Biopharma Closes Manufacturing Facility; And More.

Also, Abbott to acquire Starlims Technologies; GSK Biologicals to form alliance with Intercell.

Company and People Notes: Also, Pfizer and Protalix enter agreement; Watson acquires Arrow Group; and more.

Also, Merck & Co. extends collaboration with Idera Pharmaceuticals; Pfizer establishes R&D center in China; more...

Readers can learn about the importance of measuring and controlling water activity in a comprehensive new book.

Particularly in a more connected world, individual contributions can make a difference.

Dumbed-down presentations and poor speaker selections are destroying a valuable industry tool.

With so many healthcare and pharmacy websites, consumers could use the agency's nod of support.

Leading experts share insight on polymorphism and crystallization.

Polymorph screening is a critical step in developing an active pharmaceutical ingredient for a pharmaceutical formulation.