
The authors describe the critical aspects of an ideal fermentation services provider.

The authors describe the critical aspects of an ideal fermentation services provider.
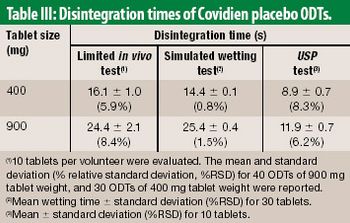
The authors propose an alternative to the USP disintegration test method. The method embraces physiological conditions of the oral cavity, as a screening tool for developing ODT products.

To meet the demands of early-stage development, contract research organizations can evaluate various dosage-form options. The author examines various methods of capsule filling, including binary blends.

Pharmaceutical companies developing new drug candidates for Hepatitis C virus infection now can test their compounds with a novel culture system that mimics the biology of HCV infection in humans.

Teva Pharmaceutical Industries and Barr Pharmaceuticals (Montvale, NJ) signed a definitive agreement under which Teva will acquire Barr, the fourth-largest generic-drug company in the world. Teva will buy each share of Barr common stock for $39.90 in cash and 0.6272 Teva shares. Based on the closing price of Teva?s shares on July 16, 2008, the price per share of Barr common stock is $66.50, and the total value of the acquisition is $7.46 billion. Teva will assume Barr?s outstanding net debt of approximately $1.5 billion.

3M Drug Delivery Systems has successfully designed a proof of concept device using a solid microstructured transdermal system for the systemic delivery of high-potency pharmaceuticals. The technology was showcased at a poster session at the annual meeting of the Controlled Release Society held this week in New York City.

The European Pharmacopeia Commission has published the General Information chapter "Potentially Genotoxic Impurities and European Pharmacopoeia Monographs on Substances for Human Use" in the July 2008 edition of PharmEuropa.

The Congressional Budget Office has released a report that provides a picture of the financial impact from the enaction of S.1695, the Biologics Price Competition and Innovation Act of 2007.
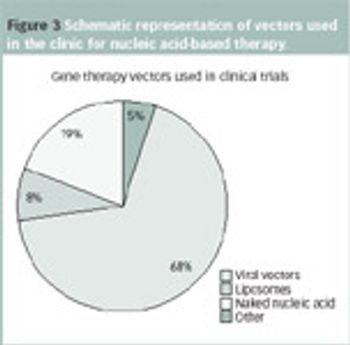
The introduction of biomolecules into cells is a key technology for research in biological sciences.

Also, Stiefel Laboratories will acquire Barrier Therapeutics, Danube Pharmaceuticals appoints Brian Levy COO, more...

The US Food and Drug Administration advised patients, caregivers, and healthcare professionals to switch to hydrofluoroalkane-propelled albuterol inhalers now because chlorofluorocarbon-propelled inhalers will not be available in the US after Dec. 31, 2008.
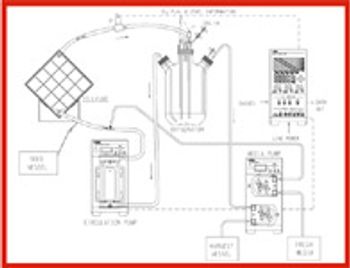
Creating a kinder, gentler manufacturing process that doesn't kill the product is the goal of process developers doing large-scale cell culture for cell therapy.
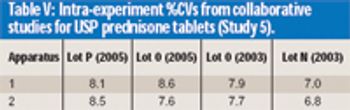
The authors demonstrate that anecdotal reports of prednisone tablet variability are inaccurate.
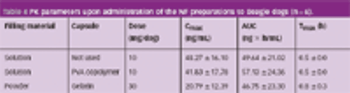
When drugs are encapsulated, electrification (the electrostatic charge of the capsule) may sometimes cause problems, such as capsule adhesion during transportation or dispersion of the capsule content in the filling process.
There are two ways in which 'difficult' samples are usually categorized: either by the problems posed by the physical nature of the post-vivo sample matrix containing the chemical entity to be analysed, or...

Once famous for coal and steel, Wales now aims to make its mark in the life sciences sector. The recent BioWales 2008 (UK) conference demonstrated how much the region has progressed, thanks to the support of the Welsh Assembly government, the EU and the enthusiasm of the Welsh biotech community. The country's bioscience sector, which comprises approximately 200 companies, grew by 18% last year and is now worth £1.3 billion (€1.6 billion) in annual turnover, employing 15–20000 people.
Scientists are giving up on a preventive vaccine for AIDS, but there are lessons to be learned.

Recent advances in SEM, particularly the incorporation of automation and software, have made simpler, lower-end SEM instruments easy to operate and have improved the capabilities of larger, sophisticated instruments.

Traditional tablet presses do not measure tablets' tensile strength, yet this characteristic strongly influences tablet quality. The author describes a compression technique that accounts for tensile strength and produces tablets with consistent weight and disintegration time.

What makes a drug ripe for respiratory delivery?
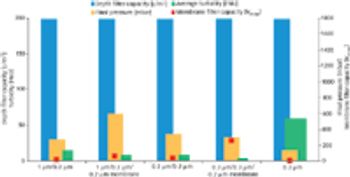
Monoclonal antibodies and recombinant proteins have increased their importance and gained success as therapeutic agents in the treatment of various diseases.

As the US biopharmaceutical industry and regulators debate new requirements for biosimilars, industry leaders are turning to analytical science to define intellectual property and business development strategies. Emerging techniques are providing previously unseen protein characterization details, giving both innovator and generics companies new weapons in the battle for future market share.
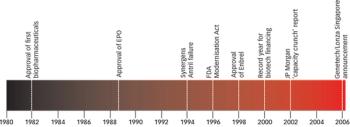
Biopharmaceuticals are the most rapidly growing segment of the pharmaceuticals market. Developing and marketing biopharmaceuticals are huge roles in almost every major pharmaceutical company's strategy. However, they are extremely complex molecules and are highly sensitive to the manufacturing processes used to produce them. These processes require exquisite control of living production systems, making, without a doubt, biopharmaceuticals one of the most challenging products of any type to manufacture.
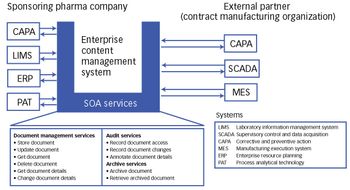
As a skipping stone creates ripples in a lake, SOA can help create benefits that quickly ripple through many other areas of the organization and partners.