
Acambis and Bavarian Nordic Vie for Smallpox Vaccine Contract

Acambis and Bavarian Nordic Vie for Smallpox Vaccine Contract

GSK Releases Flu Vaccine Production Strategies

US Government Orders 2M Doses of Avian Flu Vaccine
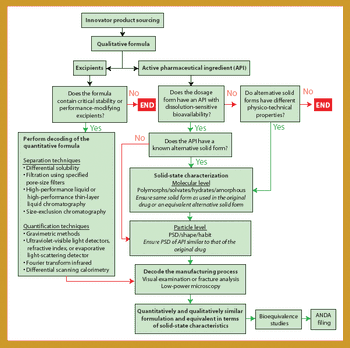
Being the first to gain the most is a fundamental principle in the generics business because several companies compete to create generics of successful products going off patent. For a generics company to maintain revenue growth in a market in which product prices continue to fall, it must secure a continuous flow of new products, with quality and speed to market being key drivers. Thus, generics companies must be highly skilled in product and process development (1), the generics business, and achieving bioequivalence-the most critical development area.
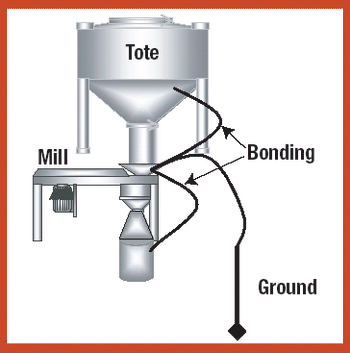
Various systems and measures can be used to safely handle and process explosive pharmaceutical compounds in a range of manufacturing procedures.

The aim of this study was to analyse the process of tablet formation and the properties of the final tablets for six different carrageenans. The carrageenans used were based on the basic types of ?-, ?- and ?-carrageenan. Microcrystalline cellulose was used for comparison. Determination of material properties, compression analysis and tablet properties were described. Water content, particle size and morphology, glass transition temperature, and crystallinity were studied. The results show that the carrageenans are predominantly amorphous fibres, which are in the rubbery state during tabletting.

Microbioreactor Array System Boost Cell Culture Capacity

Protein Refolding Technology Improves Yields

Able Labs Files for Chapter 11

Chiron Cuts Supply of Flu Vaccines Made in Germany; Liverpool Plant Under Inspection

Able Interim Chief Resigns Amid Drug Recall

A stepwise, process risk-assessment approach can facilitate the identification and understanding of critical process parameters, quality attributes, and in-process controls. This approach can lead to more use of science- and risk-based regulatory practices to simplify the regulatory requirements for changes to synthetic processes and to support the underlying quality systems that ensure compliance.

Can macromolecular processes learn from small-molecule experience? Burdened by exploding bioreactor productivity, architects of downstream bioseparation technology are looking into the drug industry's past for inspiration, while small-molecule companies adopt techniques pioneered by biotechnology. (The first of three articles on the current state of separations.)

FDA Posts Q5E Biotech and Biological Products Comparability Guideline

Self-Assembly Nanotechnology Improves Microencapsulation

Once considered mainly an afterthought in a company's lifecycle-management strategy, controlled-release dosage forms are now positioned at the forefront of many formulation strategies. In contrast to drug discovery, formulation work focuses not only on the intricacies of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API), but also on fine-tuning the excipients, the release profile, and the delivery mechanism to provide optimal therapeutic benefit. Because of their wide range of applications and functionalities, especially in controlled-release therapies, polymers are among the most widely used excipients.

Wet granulation is a size-enlargement process in which a liquid is used to achieve the agglomeration of solid particles. Agglomeration improves particles' tableting properties by rendering them free-flowing, nonsegregating, and suitable for compression (1).
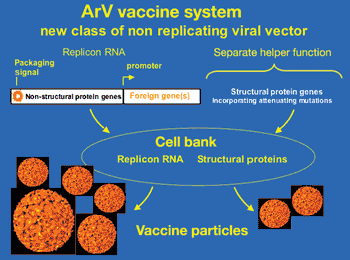
Vaccine developers are using novel drug delivery methods that offer advantages over traditional techniques such as improved immunogenicity, better stability, specific control over antigen release, and a wider pool of targeted diseases.

Vaccine developers are wrking on new drug delivery systems that offer improved immune responses, better stability, and a wider pool of targeted diseases.

A ready-to-fill closed vial can improve aseptic filling quality and reduce process complexity.
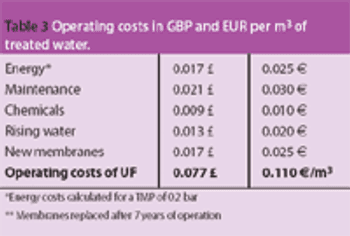
Pure water is a raw material of particular importance to the pharmaceutical industry. Drinking water is the basis for the treatment of water for pharmaceutical applications; it is the starting point for the production of the various pharmaceutical water qualities, such as purified water, highly purified water and water for injection.

The complete elimination of human-derived contamination is possible only with the elimination of human intervention.

The appropriate barrier system should be selected using a logical, risk-based approach, with awareness of all the possible sources of contamination.

Crucell and NIH Sign Ebola Vaccine Manufacturing Contract

HHS Awards $97-Million Vaccine Development Contract