
We really knew what we were doing-until we opened the column for a routine repacking.

We really knew what we were doing-until we opened the column for a routine repacking.
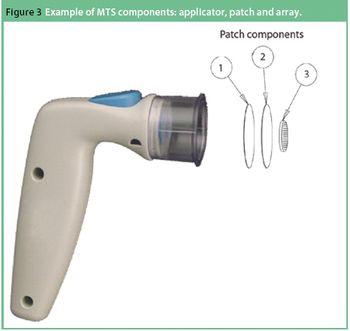
The needle and syringe have long been the standard delivery technology for vaccines. However, a confluence of market factors is driving new interest in alternative delivery systems that hold the potential to meet one or more of the following goals: improved antigen utilization, higher quality immune response, better stability and improved patient acceptance. Of particular interest are microneedle systems, otherwise referred to as microstuctured transdermal systems (MTS), that provide for targeted delivery of the vaccine formulation directly to antigen-presenting cells within the epidermis. This article provides a brief overview of MTS technology with an emphasis on solid-coated MTS for vaccine delivery.

EFPIA's 'Mock P.2' document aims to show how the role of 'quality risk management' and process analytical technology as an enabler for quality by design can be presented in a common technical document format. This article summarizes the main features of this document, and explains the key concepts and principles used.

London (Nov. 22)-The European Medicines Agency reports a defect in some vials of Herceptin (trastuzumab), the anticancer treatment by Roche, which have been distributed in Europe. As a result, The EMEA's Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use outlined a plan, formulated in conjunction with Roche, for the visually reinspecting and replacing defective vials.

Argonne, IL (Nov. 9)-Researchers from Argonne National Laboratory?s Chemistry Division and Xradia have developed a novel X-ray microscopy technique that allows molecular observations of the reactivity of solid surfaces at the nanometer scale, including interfacial reactions such as ion adsorption and catalytic reactions.

Celsis deploys ATP bioluminescence to accelerate microbial detection in pharmaceutical manufacturing.

Over-the-counter drug maker Perrigo Company issued a voluntary recall of certain lots of store-brand acetaminophen 500-mg caplets that could contain trace amounts of metal particulate. Approximately 11 million bottles of acetaminophen are affected by the recall.

Mystic, CT (Oct. 26)-Kenneth G. Chapman died at his home here on Oct. 26. He was 79. The cause was pancreatic cancer

AAPS, San Antonio (Oct. 31-The advantages of ultra-performance liquid chromatography over traditional high-performance liquid chromatographic were the center of the presentation, ?Strategies for Rapid Chromatographic Method Development from Preclinical to Phase 3,? by Charanjeet Jassal of Wyeth Pharmaceuticals.

AAPS, San Antonio (Oct. 31)-Industry and regulatory agency concerns over process variability have prompted both groups to take a closer look at analytical method transfer processes.

AAPS, San Antonio (Oct. 30)-Although the analysis of impurities in drug substances and drug products is not a new topic, new regulations are increasing concern in the industry.

San Antonio, TX (Nov. 1)-Though the US Food and Drug Administration's final guidance on process analytical technology (PAT) was published in Sept. 2004, companies are still unsure about how exactly to implement PAT in their processes.
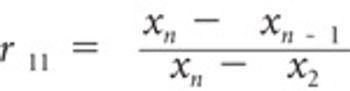
Outliers may provide useful information about the development and manufacturing process. Analysts use various statistical methods to evaluate outliers and to reduce their impact on the analysis. This article describes some of the more commonly used identification methods.
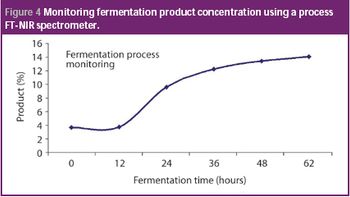
Quality by design and PAT approaches are increasingly being used for the biotech manufacturing of medicines. Complex manufacturing processes can not only be controlled using PAT principles, but optimized with respect to both product quality and economic value. This column describes how the fermentation process is often the first to benefit from this type of implementation.

Rockville, MD (Sept. 28)-The US Food and Drug Administration has released the draft guidance for industry ?Characterization and Qualification of Cell Substrates and Other Biological Starting Materials Used in the Production of Viral Vaccines for the Prevention and Treatment of Infectious Diseases.?

More CMOs look to proprietary delivery technologies to enhance profitability.
The presence of very low levels of residues (including solvents) in excipients is becoming an important issue for users, and the presence of very low levels of ?non-lactose? species in DPI lactose may pose challenges to suppliers and users.

Arlington, VA (Sept. 12)-At the American Association of Pharmaceutical Scientists meeting here, "e;Real World Applications of PAT and QbD in Drug Process Development and Approval" (Sept. 11-12), chemical engineer and process modeler Michael L. Thompson, PhD, described how Procter & Gamble (West Chester, OH, www.pg.com) applies these mathematical tools to increase product quality and reduce development and trouble-shooting time for consumer and pharmaceutical products.

Washington, DC (Sept. 12)-The Office of New Drug Quality Assessment (ONDQA) in the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) has approved one new drug application (NDA) under its CMC Pilot Program and has two more applications are under review. The pilot was established last year to provide an opportunity for FDA and industry to explore strategies for including Quality by Design (QbD) principles and process analytical technology approaches in regulatory submissions, explained ONDQA deputy director Chi-wan Chen at the PDA-FDA Joint Regulatory Conference here

As the pace of product development accelerates, the approach to dissolution-method development must advance beyond a manual method and an assay. A natural progression of the method-development process must include the transfer of the manual method onto automated instrumentation.

I recently embarked on a quest: to investigate industry's use of the words, "generic" and "biosimilar" when describing a biologic molecule. An English major at heart, I was wrapped up in a news story that was partly about science, partly about words.
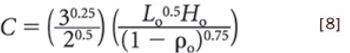
Quantitative data from the literature show strong relationships among average particle size, powder densification, tensile strength, and hardness.

A group of researchers from Georgia Institute of Technology (Atlanta, GA) are using high-throughput ionization techniques to identify and measure the ingredients in counterfeit drugs.

This article summarizes changes to the Akers–Agalloco aseptic processing risk analysis model (first presented in Pharmaceutical Technology's November 2005 issue) as well as some of the underlying thinking behind the revision. The simplified model makes the method easier to use because of its greater flexibility of environmental control practice. It maintains the emphasis on human activity as the primary consideration in risk management for aseptic processing.

Accurate characterization of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) is a critical part of the drug development process. The approaches used to characterize APIs with respect to structure, identification of impurities, and the solid-state were discussed by Andrew C. Kolbert, manager, molecular structure and spectroscopy, Cardinal Health (Dublin, OH).