
Orally disintegrating tablets (ODTs) continue to attract attention as an alternative to conventional oral dosage forms.

Orally disintegrating tablets (ODTs) continue to attract attention as an alternative to conventional oral dosage forms.
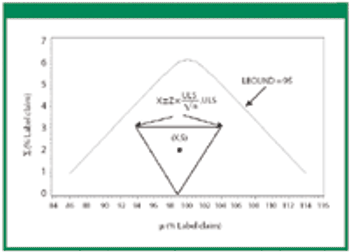
Revisions to the United States Pharmacopeia's (USP) uniformity test require manufacturers to establish new acceptance limits. The authors present their method for calculating acceptance limits consistent with USP's revised content-uniformity test requirements.

High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is a powerful tool for the enantioselective separation of chiral drugs. However, the selection of an appropriate chiral stationary phase (CSP) and suitable operating conditions is a bottleneck in method development and a time- and resource-consuming task. Multimodal screening of a small number of CSPs with broad enantiorecognition abilities has been recognized as the best strategy to achieve rapid and reliable separations of chiral compounds. This paper describes the generic screening strategy developed at Johnson & Johnson Pharmaceutical Research and Development to successfully develop enantioselective HPLC methods for chiral molecules of pharmaceutical interest.
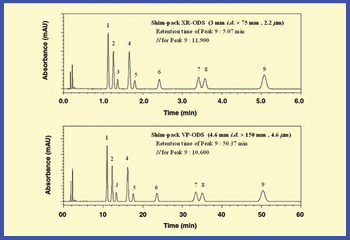
The authors review methods for reducing analysis time and increasing throughput that are reliable and maintain data integrity.
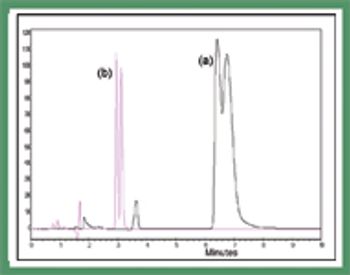
Polysaccharide-based chiral stationary phases have been developed that comprise chiral selectors immobilized on their support rather than being physically coated. These materials are completely solvent stable, thereby increasing selectivity and and enabling the development of new chiral selectors that have been too unstable in a coated form for general use.

The combination of supercritical fluid chromatography with chiral separation media offers several analytival advantages over traditional liquid chromatography techniques.
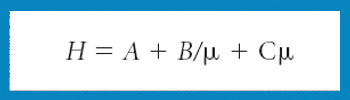
Ultrahigh pressure liquid chromatography maximizes efficiency, but, as defined by the resolution equation, the stationary phase is still a crucial consideration when attempting to resolve mixtures of compounds.

High performance liquid chromatography has become an efficient technique at the production scale, and simulated moving bed chromatography provides several benefits during processing.
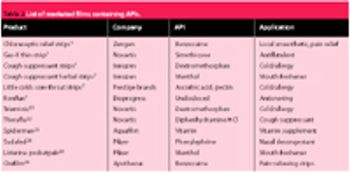
The authors consider the advantages of using rapidly dissolving films to accurately and effectively deliver pharmaceutical ingredients, with an emphasis on the importance of controlling moisture content and drug loading during formulation development.
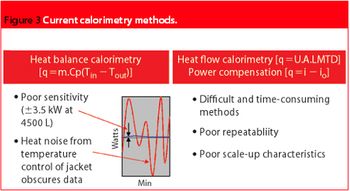
To date, calorimetry has not been given a fair trial in the PAT arena. Recent advances in reactor technology and design will ensure that real-time calorimetry is the present and future of PAT.
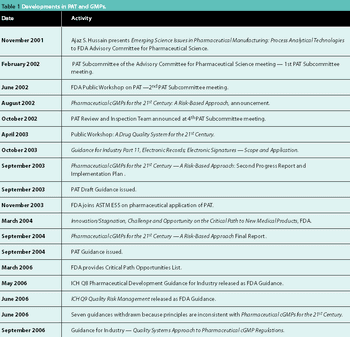
Recent regulatory initiatives have emphasized the need to improve pharmaceutical manufacturing. PAT marked the beginning of a number of regulatory efforts to encourage innovation and a transition towards science-based manufacturing. This article reviews the progress of the regulatory initiatives and describes two significant research initiatives to develop a future pharmaceutical manufacturing environment based on scientific understanding of pharmaceutical materials and processes.

Company and People Notes: Evotec and Renovis enter agreement, Amgen to lay off 675 workers, more.

Company and People Notes: Catalent expands Bolton, UK, warehouse; Biotica appoints Edward E. Hodgkin as CEO and director; more.

454 Life Sciences, part of Roche, and researchers at Columbia University identified a virus associated with the deaths of 2.4 million honey bee colonies.

Company and People Notes: Baxter and Halozyme Expand Relationship, Crucell Names COO, More.

The US Food and Drug Administration’s Interagency Working Group on Import Safety released a Strategic Framework based on a cost-effective, risk-based approach for ensuring the safety of products exported to the United States.

Appendix: definitions and regulations, Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act; Appendix: definitions and regulations, Title 21 Code of Federal Regulations; Appendix: definitions and regulations, Compliance Policy Guides

This article presents collaborative positions among excipient manufacturers, drug product manufacturers, and members of the US Pharmacopeia on key issues pertaining to the control of pharmaceutical excipients stemming from a recent Pharmaceutical Quality Research Institute workshop.

Larger and strategic sampling and testing plans can improve process understanding and characterization.
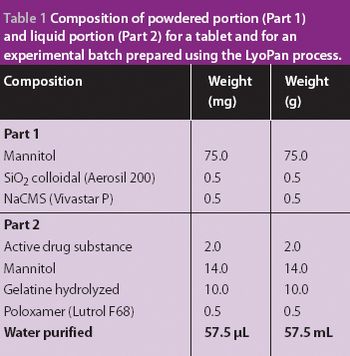
A new economical method for producing fast-melting lamina-like dosage forms.
In biomanufacturing, multiple sensors provide a wealth of data that could be used to enhance process understanding and assist in performance improvement. This article looks at how to move from a data-rich environment to one where the data are translated to useful information that leads to knowledge and, ultimately, process improvements.
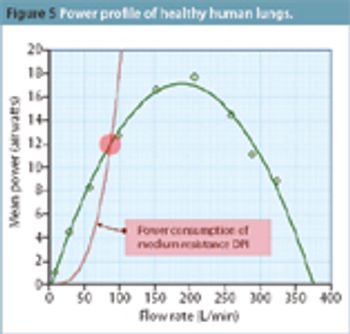
This article investigates how the industry can test inhalers in a way that is most representative of typical use.
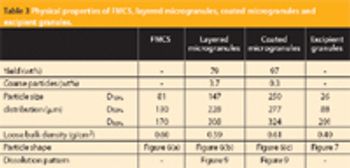
This article describes how rapidly disintegrating tablets containing a large quantity of an intensely bitter drug were successfully developed with a suitable level of masking, tablet hardness, disintegration property, dissolution profile and mouth feel.

A new Raman spectroscopic method to detect magnesium stearate in powder blends and tablets is described. High-volume pharmaceutical manufacturing requires the use of lubricants to facilitate tablet ejection from compressing machines. However, lubricants may also bring a number of undesired problems that have been widely documented in pharmaceutical scientific literature. New analytical methods are needed to understand lubrication and provide process knowledge in support of FDA's process analytical technology initiative. The detection of magnesium stearate in lactose, mannitol, corn starch and other commercially important excipients is reported. The Raman spectroscopic method has a detection limit of about 0.1% (w/w) based on the 2848 cm-1 band that corresponds to the symmetric stretch of the methylene group in magnesium stearate.

Identifying polymorphs is a crucial part of the drug-development process as researchers forward select methods to improve detection.