Risk assessment and management applies to technical matters as well as to interactions between organizations.

Risk assessment and management applies to technical matters as well as to interactions between organizations.

The UK Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA, London) has reissued its recall of a specific batch of counterfeit ?Lipitor? 20-mg tablets. MHRA, in conjunction with Pfizer (New York City, NY), first issued the recall of batch number 004405K1 in July 2005. The new recall is in response to the discovery of more packages of the counterfeit drug in the United Kingdom.

A group of researchers from Georgia Institute of Technology (Atlanta, GA) are using high-throughput ionization techniques to identify and measure the ingredients in counterfeit drugs.

The US Food and Drug Administration?s Counterfeit Drug Task Force (Rockville, MD, www.fda.gov) is recommending regulatory actions and the implementation of new technologies for reducing the risk of counterfeit drugs entering the United States. The group has followed up on its original 2004 report, in which it outlined the framework for protecting the public from counterfeit medicines, and an updated 2005 report with a third document encouraging electronic pedigrees, improved traceability in the drug supply chain, and the adoption of radio-frequency identification (RFID) tools.

Thermal effusivity and power consumption may help predict granulation end point in high-shear granulators. In this study, power consumption was monitored and compared with percent relative standard deviation (RSD) on thermal effusivity measured at-line. Lactose monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, and magnesium oxide were granulated, and the effect of load size on granule growth in a fixed-volume granulator was evaluated using three load levels. Load size, liquid addition rate, and impeller speed were measured, and the correlation among RSD on effusivity, power consumption, mean granule specific surface area, and granule compressibility index were determined.

Predictable outcomes lead to greater manufacturing efficiency and speed time to value.

In the face of spiralling R&D costs, currently estimated at $800 million to produce a new drug, the discovery industry is constantly searching for ways to keep expenditure low, increase productivity and meet ever-stricter guidelines imposed by regulatory bodies.

Seven automation suppliers have joined with users on the Instrumentation, Systems, and Automation Society (ISA, Research Triangle Park, NC) "Wireless Standards for Automation (SP100)" committee to develop wireless network structures for manufacturing plants.
Using Bezier curves, an experimental process controller has been developed for biosynthesis applications in which the inactivity of a pH-sensitive enzyme must be decreased. By taking into account various control scenarios of pH and growth rate, as well as the physical and chemical characteristics of the environment, a suitable human-machine interface can be developed.

This article examines the development of a business case to secure coveted funding for a LIMS implementation. Information on hard cost savings and soft benefits of implementing a LIMS system, and managing the compilation of the cost justification are covered.

A laboratory information management system (LIMS) can control, manage, organize and document information thus saving time and money.
The need to curb drug counterfeiting is spurring development of track-and-trace and product authentication technologies.
All sectors of manufacturing are under continual pressure to bring new products to market quicker, stealing a march on the competition and maintaining their revenue stream.

The pharmaceutical sector is a billion dollar industry with a huge responsibility towards its customers and investors. The main tools for fulfilment of this responsibility are ensurance of compliance and maintenance of control. It is a time-consuming job to uphold these responsibilities, and many important decisions regarding this subject are taken every day. It is important to make carefully considered decisions and follow them up. It is also essential to stop once in a while and reconsider their validity and relevance.

GSK Begins RFID Pilot Program

Implementing a PAT Strategy

Secondary sensors help protect feedback control systems from the effects of sensor drift.

If delaying the project has little consequence then you should probably not run the project in the first place.

Baselines are one of the most useful tools in the 'validation toolbox'. They can be used for a variety of tasks with great success. This article will examine how they can be used and for what.
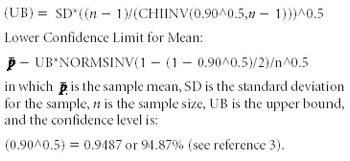
Using the Bergum Method and the MS Excel software program, the author determines the probability of passing the USP dissolution test.

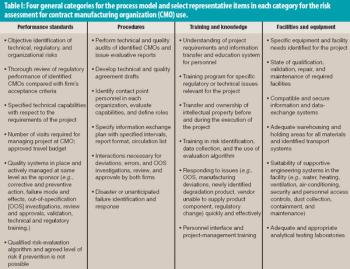
Contract manufactures are faced with multiple challenges when determining whether to implement process analytical technology into their clients' or their own infrastructure.
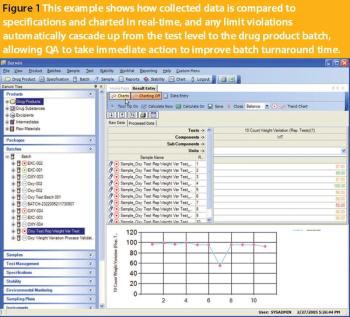
To produce an application or solution for a specific domain, a vendor must demonstrate a thorough understanding of the domain and its specific challenges.
A new Good Automated Manufacturing Practice (GAMP) guide on IT Infrastructure Control & Compliance was launched in Chicago (IL, USA) 23 August 2005.1 The guide is intended to support pharmaceutical companies in their effort to establish a well-defined and compliant infrastructure. This article discusses different aspects of the guide that may support your organization in getting — and keeping — your infrastructure under control.

The process analytical technology (PAT) initiative has been percolating at the US Food and Drug Administration for a long time, explained FDA's John E. Simmons at the AAPS Annual Meeting and Exposition on Wednesday. "If you think of PAT as an isolated set of applications, I think you are missing the point," Simmons said. "The FDA would like PAT to become commonplace?not to be an initiative, but common practice."

As a pharmaceutical formulation tool, molecular simulation is currently in its early infancy. Nonetheless, presenters at Wednesday?s AAPS Annual Meeting and Exposition demonstrated that the technology is beginning to attract some interest. The topic was discussed in a presentation titled "Application of Molecular Simulations to Formulation Development and Stability Prediction."