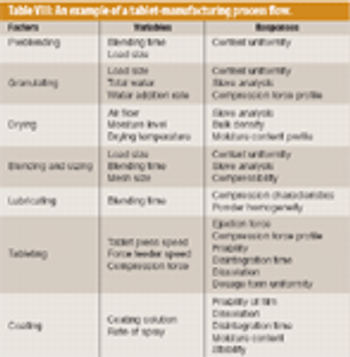
Almost all pharmaceutical manufacturing processes require handling and processing cohesive powders. The application of sufficient shear (i.e., the total deformation that the bulk of granular material undergoes under applied shear stress) is an essential factor in such processes. Sufficient shear is required to mill and de-lump materials, achieve sufficient flow, and homogenize cohesive ingredients. Shear mixing plays a critical role in the blending of dry powders, particularly for those that contain a minor cohesive component such as a solid lubricant or a drug. This mechanism is necessary to achieve a satisfactory homogeneity and disintegrate possible agglomerates. Excessive shear can be disadvantageous, however, and can lead to electrostatic buildup, attrition, and overlubrication.