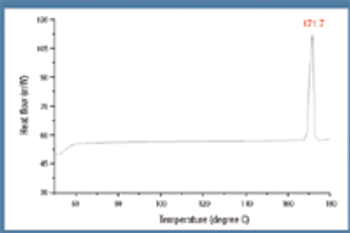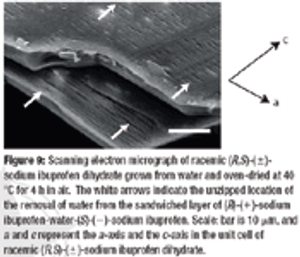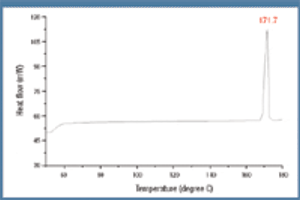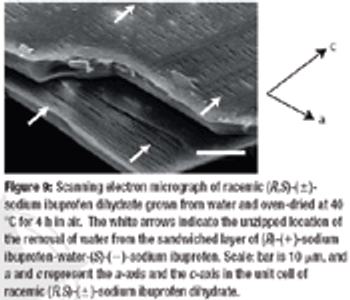
The racemic compound (R, S)-(±)-ibuprofen is a popular and well understood active pharmaceutical ingredient, but it has several disadvantageous formulation properties such as poor solubility, low melting point, and potential esterification with excipients containing an hydroxyl group. The authors investigate the use of an (R, S)-(±)-ibuprofen salt to evaluate these problems using various analytical methods to determine the polymorphism, crystallinity, and drying scheme.