
The FPC50W is an aseptic filling system with full or partial stoppering and crimp capping of vials, delivering fill volumes ranging 0.1ml to 100ml and filling accuracy of +/- 0.5%.

The FPC50W is an aseptic filling system with full or partial stoppering and crimp capping of vials, delivering fill volumes ranging 0.1ml to 100ml and filling accuracy of +/- 0.5%.

PharmTech speaks to Ray O'Connor from the National Institute for Bioprocessing Research and Training (NIBRT) for an overview of aseptic processing.

Room-temperature sterilization using nitrogen dioxide gas provides benefits for sterilizing the external surfaces of single-dose, parenteral drug containers.

An efficient cleaning cycle begins with equipment and automation-system design.

How to avoid invisible and airborne contamination.

Closed-vial technology is an alternative to traditional glass vial filling that reduces the risk of contamination for the patient, simplifies the filling process, and provides easier handling for healthcare providers.

FDA has released a final guidance describing cGMP for preparing media fills for validation of aseptic preparations for positron emission tomography drugs.

Contamination is almost always related to human error and there is a clear drive to reduce human implications in aseptic operations. This can be achieved in multiple ways.

The future, and increasingly the present, for aseptic operations is isolated robotics. Companies that wish to gain competitive advantages in their operations are stepping up and taking notice.

Henrik Schwartzbach, senior process technologist at GEA Niro, explins why spray drying is seeing increased uptake in the pharma industry.
![Rivera-Fig-4-new[2]web-731308-1408618780125.jpg](https://cdn.sanity.io/images/0vv8moc6/pharmtech/c5b3bd34e31edbde4e6a56be25a83c3d7a998f32-504x275.jpg?w=350&fit=crop&auto=format)
The author describes the components that make up a clean-in-place system and how the system should be built to ensure efficiency.
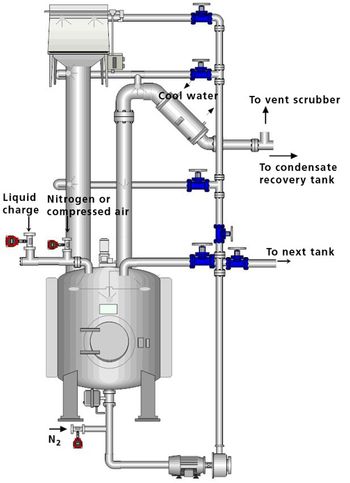
The author describes the benefits and challenges inherent to cleaning in place (CIP). The article also describes the development and validation of a CIP cycle.

To help you get up to speed with the ins and outs of the amended version of Annex 11, which will come into effect on 30 June 2011, PTE brings you two articles that take a close look at the amendments.

Normal industrial practice is to control foot-borne contamination with adhesive peel-off disposable mats, but polymeric contamination-control flooring is becoming increasingly popular.

Changing or upgrading cleanroom gloves requires time and due consideration. A good decision could improve employee satisfaction and product yields, but a bad decision could necessitate millions of dollars worth of rework, recalls, and rejects if the gloves don?t perform as expected. Personnel should consider various criteria to choose the best glove for their cleanroom.

The author details the factors in formulation design, requirements in facilites and equipment, and validation criteria for aseptic formualtions.

Investing time and money in auditing and optimizing a steam system can pay off quickly, especially because the costs of energy, maintenance, and downtime are steadily rising.

Devices that measure relative humidity (e.g., sensors and transmitters) play a relatively small role in cleanroom management, but their failure can cause significant problems. Operators should bear several factors in mind to ensure that sensors function properly and maintain the appropriate humidity.

A novel cleanroom apparel design incorporates modern concepts to help minimize contamination. Take a tour of the design.
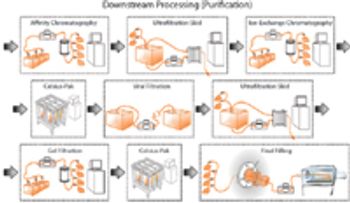
The authors discuss current and future disposable technologies and outline the validation and qualification steps that would be required for a possible disposable process stream.

The authors review the role of automation in aseptic processing and describe their experience in implementing advanced technologies, including the use of isolators and robotics.
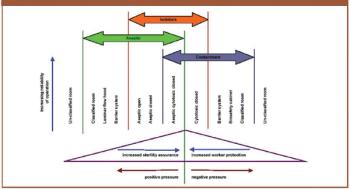
The author discusses the key issues to consider when using isolators such as containment, protection of personnel, the efficiency of biodecontamination cycles, sterility assurance levels, barriers and their integrity, and environmental impact.
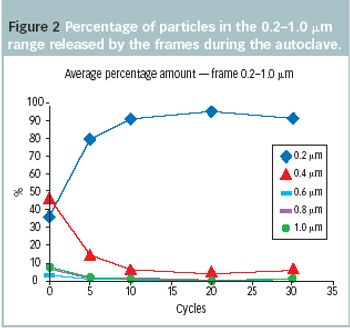
Hood, suit, faceplate, cover shoes, gloves: these are the necessary items of clothing when operating in A-and B-grade areas.

In light of the rising price of stainless steel components and facility construction, pharmaceutical companies are increasingly using disposable components and systems in their manufacturing processes.

The US Food and Drug Administration issued a rule that clarifies its requirements for current good manufacturing practices for aseptic processing, water standards, and verifications standards.