
Also, Roche to end HIV/AIDS research program, WuXi PharmaTech makes appointments, more...

Also, Roche to end HIV/AIDS research program, WuXi PharmaTech makes appointments, more...
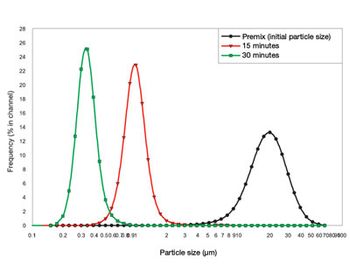
Creating nanoparticles can be challenging and requires appropriate equipment and techniques. Media milling or grinding is the best-established manufacturing method for nanoparticle production.

A pharmaceutical company's information-technology infrastructure could facilitate the appraisal of the performance of contract manufacturing organizations.

PharmTech's monthly newsletter, Equipment & Processing Report, reviews the Editor's Picks for the July 2008 edition from Parker Fluid Control Division and Watson-Marlow Bredel.

Also, Catalent Pharma Solutions to collaborate with One World Design and Manufacturing Group, Bioheart appoints Howard J. Leonhardt as CEO, more...

The European Pharmacopeia Commission has published the General Information chapter "Potentially Genotoxic Impurities and European Pharmacopoeia Monographs on Substances for Human Use" in the July 2008 edition of PharmEuropa.

The European Pharmacopoeia Commission adopted revised monographs for heparin calcium and heparin sodium to strengthen the level of testing required for quality control.

Change control in life-sciences organizations is a critical business issue in terms of risk, safety, and performance. The author examines common shortcomings in change control when implementing non-enterprise solutions and the functionality derived from enterprise-level change control.

Also, Covance and WuXi PharmaTech to form contract research joint venture in China, Covidien makes appointments to its Pharmaceutical Products and Imaging Solutions businesses, more...

Molecular Profiles created a poster that demonstrates the efficacy of its "nanoPASS" (nanoscale predictive analytical screening solution) technique to characterize an active pharmaceutical ingredient's (API) surface energy.

After a one-year delay in its implementation, the US Pharmacopeia Chapter 467 "Residual Solvents" is now official.

The Congressional Budget Office has released a report that provides a picture of the financial impact from the enaction of S.1695, the Biologics Price Competition and Innovation Act of 2007.

President Bush signed H.R. 2642, the Supplemental Appropriations Act of 2008, which provides $150 million to the US Food and Drug Administration for medical-safety and drug-safety activities.

The US Pharmacopeia (USP) posted revised monographs for heparin sodium and heparin calcium on its website.

Biomedical researchers at UT Southwestern Medical Center and nanotechnology scientists at UT Dallas are collaborating on a study that seeks to selectively kill cancer cells using monoclonal antibodies to coat carbon nanotubes that heat up when exposed to near-infrared (NIR) light.

Also, Stiefel Laboratories will acquire Barrier Therapeutics, Danube Pharmaceuticals appoints Brian Levy COO, more...

A review of an event that gathered in Cork (Ireland) the crème-de-la-crème in the world of excipient technology.

Also, Patheon to expand Puerto Rico facility, Creabilis Therapeutics appoints Tony Wilson CEO, more...

Effective July 1, 2008, the Office of Generic Drugs (OGD) will require abbreviated new drug applications (ANDAs) to include data that demonstrate the manufacturer's control of residual solvents.

The US Food and Drug Administration and the European Medicines Agency will collaborate in efforts that would allow drug companies to submit results of seven new drug-safety tests.

To choose the appropriate conveying system, a pharmaceutical manufacturer needs a thorough knowledge of the benefits and limitations of each conveyor type. The following overview compares several types of systems.

PharmTech's monthly newsletter, Equipment & Processing Report, reviews the Editor's Picks for the June 2008 edition: Esco Technologies and Hawk Measurement

Manufacturers have stopped seeing disposable containment as an ad hoc solution, and the technology increasingly incorporates thoughtful design and engineering. The future promises to bring more changes and new applications for disposable containment technology.

In an assessment report about medicinal products containing heparin, the European Medicines Agency (EMEA)'s Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) said it could not draw firm conclusions about the level of risk associated with unfractionated heparins (UFH) contaminated with oversulfated chondroitin sulfate (OSCS). Nevertheless, CHMP recommended that contaminated lots be withdrawn completely.

Also, Shire voluntarily recalls ADHD patch Daytrana

Also, Pall plans expansion in South America, Anthony Clarke joins Alexza Pharmaceuticals, more...

The transatlantic cooperation of the European Commission, the European Medicines Agency, and the US Food and Drug Administration was recognized at the Second Meeting of the Transatlantic Economic Council, held mid May in Brussels. The TEC is tasked with overseeing and accelerating government-to-government cooperation to advance economic integration between the United States and the European Union.

The US Food and Drug Administration advised patients, caregivers, and healthcare professionals to switch to hydrofluoroalkane-propelled albuterol inhalers now because chlorofluorocarbon-propelled inhalers will not be available in the US after Dec. 31, 2008.

Brief pharmaceutical news items for June 2008.

University of Calgary biochemists used computer simulation in a new toxicity study to predict how "buckyballs," carbon-60 soccer ball-shaped nanomolecules, could damage animal cells.