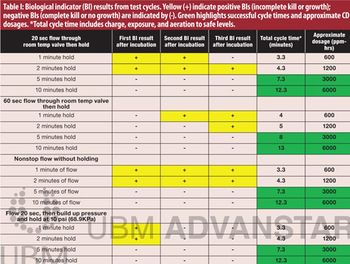
A chlorine dioxide sterilization cycle was developed for a novel split-valve aseptic powder transfer device.

A chlorine dioxide sterilization cycle was developed for a novel split-valve aseptic powder transfer device.

Soft sensors are powerful tools that can be used along with spectroscopic instruments in on-line measurement.

Continuous manufacturing will not work for all pharmaceuticals, but the right infrastructure, senior management support, and planning from the earliest stages of drug development could eventually allow up to 80-90% of small-molecule APIs to be made continuously, says Paul Sharratt, head of process science and modeling at Singapore’s Institute of Chemical and Engineering Sciences.

A venture between GEA and Siemens aims to familiarize more pharmaceutical companies with more modern control and continuous processing.

Solid dispersions based on organic polymers can have stability issues. Inorganic solids, especially those based on silica chemistry, may be suitable alternatives to organic polymers due to their pre-formed pore system, high absorptivity, and commercial availability in pharmaceutical quality. Mesoporous granulated colloidal silicon dioxide has been studied with class II and IV actives of the Biopharmaceutics Classification System for its ability to improve dissolution. Using suitable formulation strategies, the dissolution of these APIs could be significantly increased. The absorption of poorly soluble APIs onto silicon dioxide can, therefore, be considered a viable formulation path to overcome solubility challenges.

This novel technology was developed in response to challenges involved in conventional manufacturing of multilayer tablets, including in-line control of the tablet weight, the tendency to delamination, direct contact between the two tablet layers, and cross contamination.

This article summarizes the evolution of the viscosity standards and their corresponding applications in the USP−NF compendia.

Process analytical technology, based on monitoring particle size distribution and tracking coating thickness measurements in real time, can be used to predict the dissolution of polymer-coated multiparticulates.

A case study reviews the reformulation and scale up of high drug load prototype using wet granulation process for a model formulation.

Click the title above to open the Pharmaceutical Technology 2017 Solid Dosage Supplement in an interactive PDF format.